Overview
Welcome to Quantexa News API — the most powerful way to aggregate, filter, and integrate global news data into your apps and models.
This technical documentation will guide you through every step of the process, whether you are a total beginner with Quantexa News API or an experienced user.
Three methods of accessing Quantexa News API
1. Search UI
The fastest and easiest way of building and testing Quantexa News API queries is using Search UI. Build your queries in seconds and when you are happy with your query, simply copy and paste the code generated.
Step 1: Getting access to News API
- Before starting, make sure you have created a News API account and have access to your App ID and Key. Subscribe to create a free account.
Step 2: Build your search
Go to app.aylien.com
Enter your username and password — contact the Quantexa support team if you don’t have your credentials.
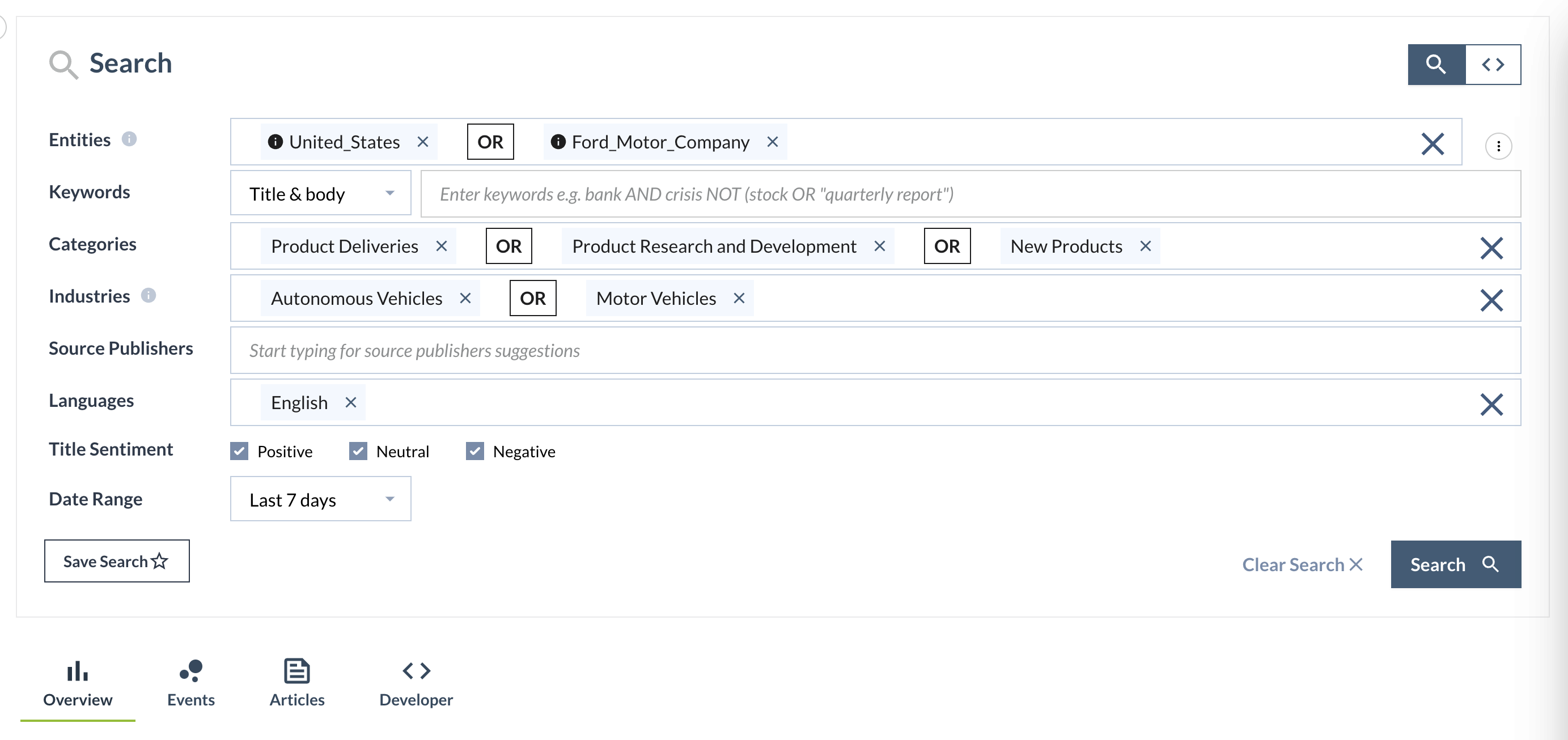
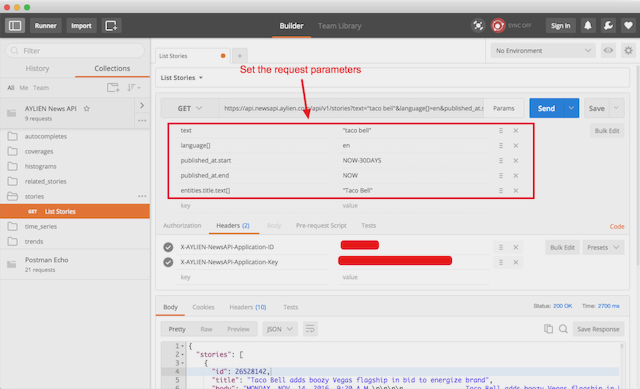
Enter your query criteria. See the sample below:
Step 3: Developer mode
- Access the developer tab. See image below:
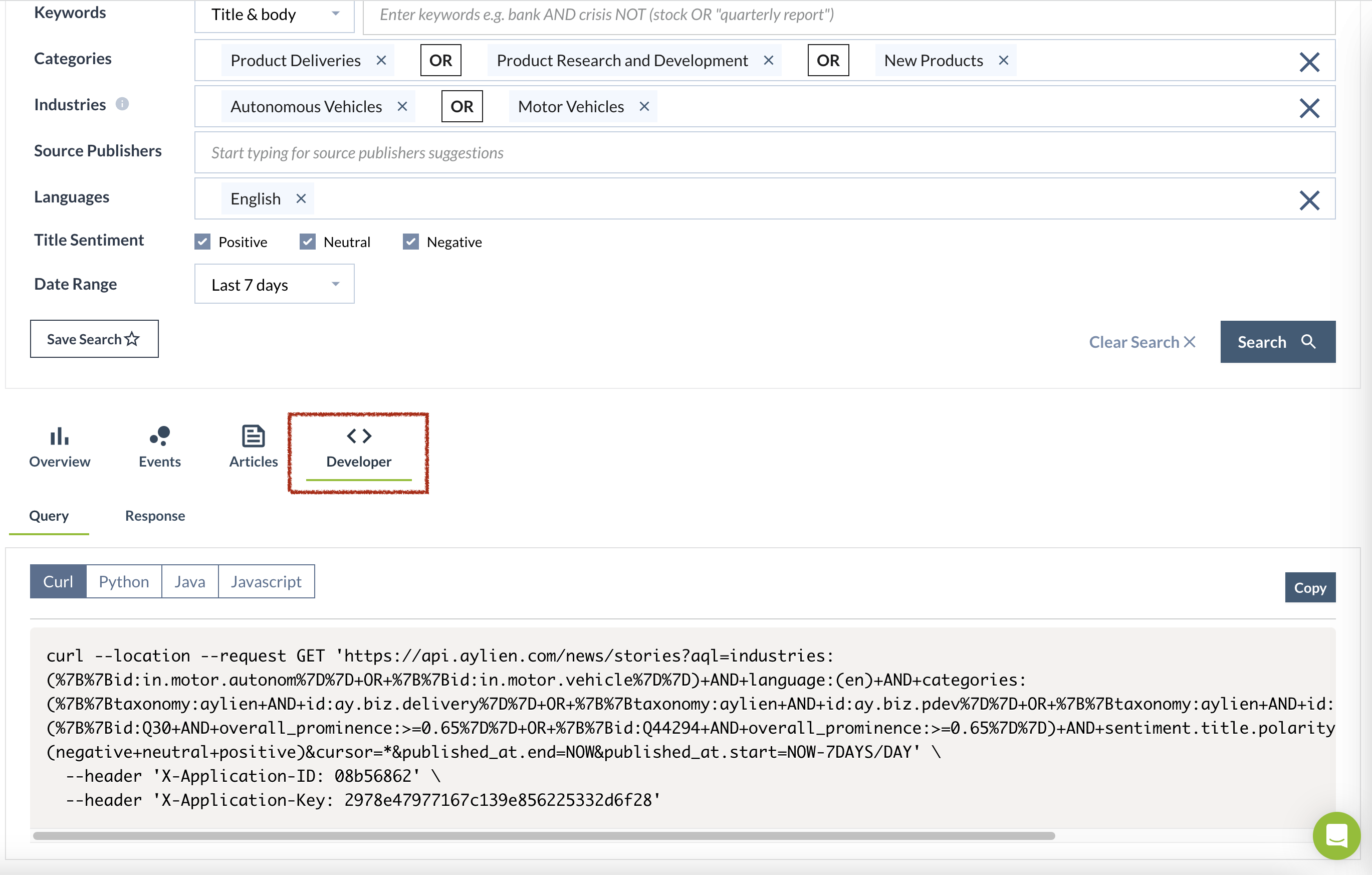
- You can copy the code from the developer tab and use your programming language of choice.
- Currently, it supports languages such as Curl, Python, Java, and Javascript.
- For more information on how to use Search UI, watch our Getting Started video for developers.
2. Postman
Postman is a quick and straightforward way of testing Quantexa News API and familiarizing yourself with its various endpoints and parameters.
Once you've downloaded and installed Postman, follow the steps below to get up and running with Quantexa News API.
Step 1: Getting access to Quantexa News API
- Before starting, ensure you have a Quantexa News Intelligence account and the username and password. Click here to create a free account.
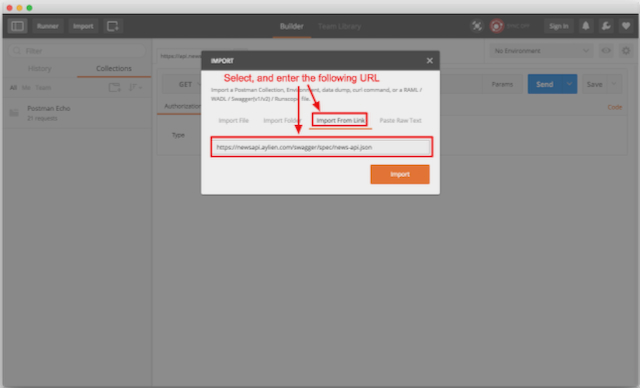
Step 2: Import API collection to Postman
Open Postman, and click the "Import" button in the top left corner.
In the Import dialogue, paste the following URL into the input box, and click Import/Enter.
URL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AYLIEN/apis/master/aylien/v6/news/api.yaml
- Once the schema (YAML file) is imported, a new collection will appear on the left panel.
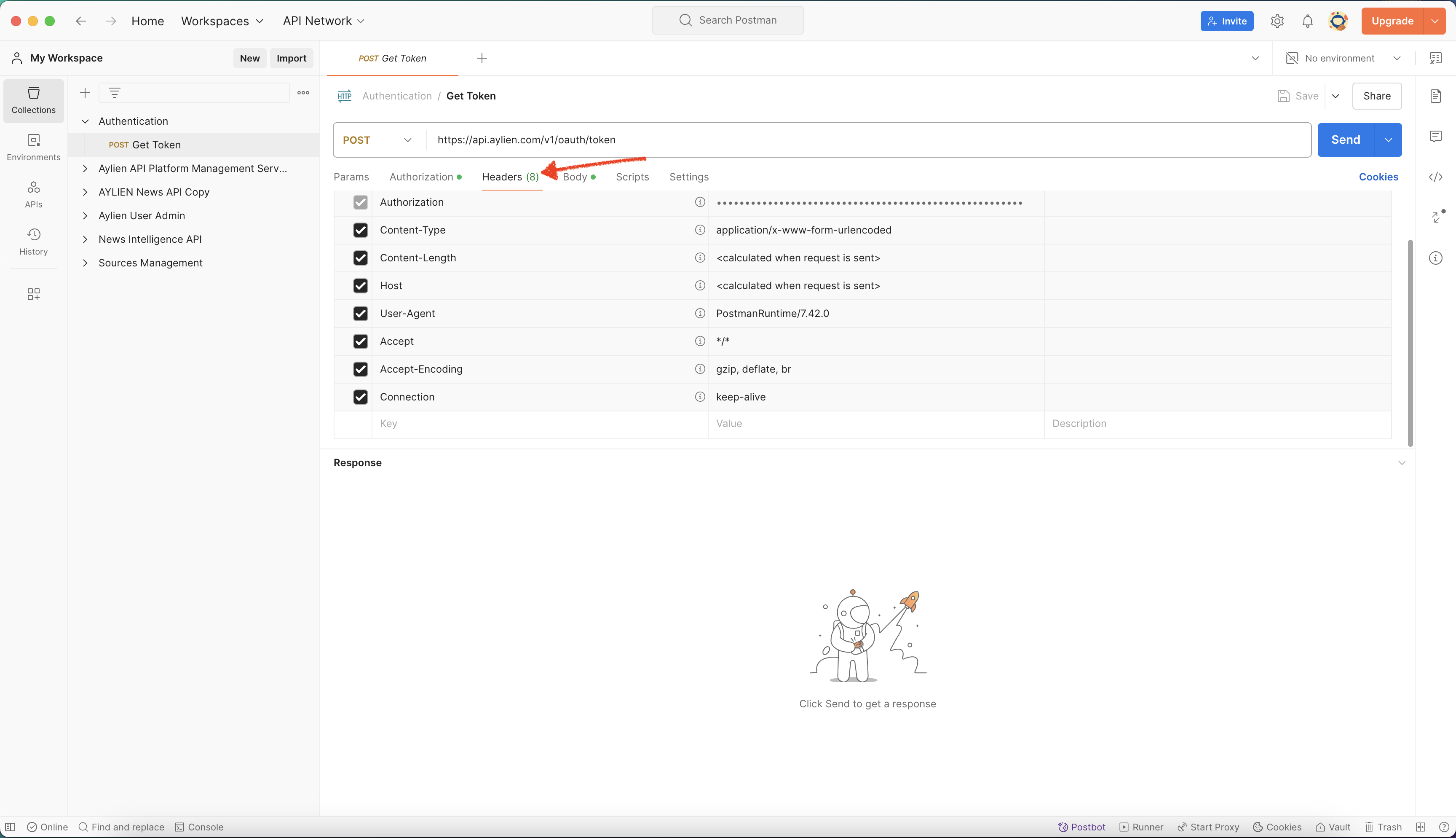
Step 3: setting up headers and body request
- Set up the headers and body of your API call request as per below.
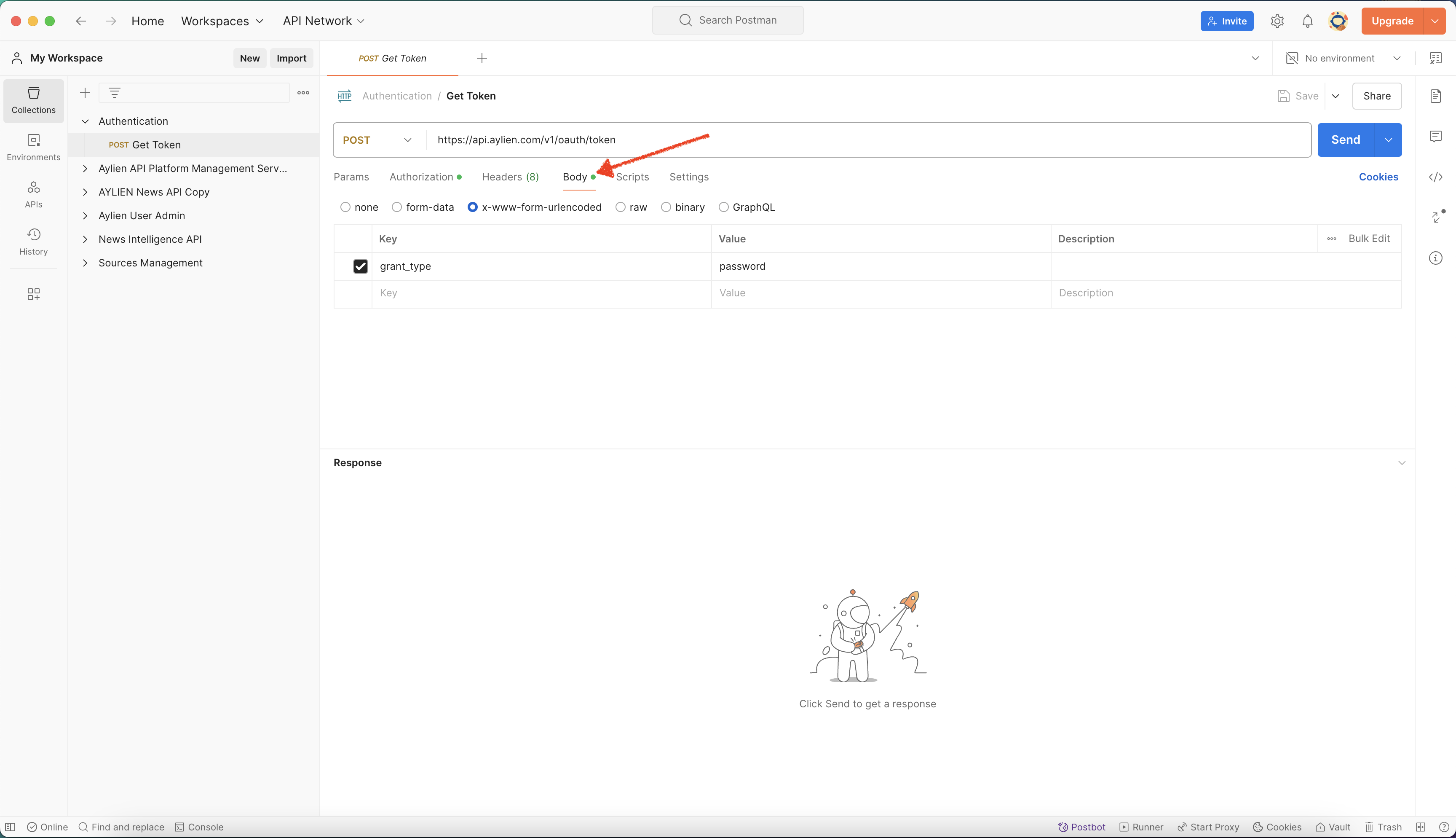
Step 4: Bearer token authentication
- Get your bearer token by calling the endpoint https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token and passing your username and password. Then copy the value from the field "access_token".
Step 5: Sending API Call
Pass the bearer token before calling the News API endpoint. It’s set on the tab “Authentication”, by choosing the option “Bearer Token” under the dropdown “Auth Type”:
Once the authentication is set, click on Send to submit the request and retrieve the results from the News API.
3. Code
Using the Quantexa News API in any programming language offers a powerful tool for developers and data analysts seeking to access news data. Its easy integration, customizable queries, and support for real-time updates simplify the process of fetching and processing news articles.
Additionally, features like sentiment analysis, entity recognition, categories, and content summarization make it versatile when using script language.
Across this documentation page, you will find many practical examples of Python requests.
Key concepts
Authentication
Bearer Token
The Quantexa News API authenticates using a bearer (access) token. The token is requested via the authentication endpoint with the account username, password, and Application ID.
Obtaining the initial access and refresh token with your credentials
Access tokens are valid for one hour. After this period, a new token must be requested. To do so, use the refresh token provided alongside the access token (as shown below).
The suggested function below will retrieve the access bearer token.
import requests
def get_token(username, password):
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token, refresh_token = token.json()['access_token'], token.json()['refresh_token']
return token, refresh_token
Usage
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
token, refresh_token = get_token(username, password)
Obtaining further access tokens using the refresh token
You can obtain a new access bearer token by sending a ´refresh token´. Refresh tokens allow for continued authentication without using your username and password. It is faster and more secure to use refresh tokens after the initial authentication (as documented above) instead of passing your username and password each time the access token expires.
Refresh tokens are valid for 24 hours. However, with every request to obtain a new access token, you will also receive a new refresh token, so there should be no need to pass the username and password again as long as you always use the latest refresh token within 24 hours.
The suggested function below will retrieve a new access token by passing a refresh token. The response will also include a new refresh token, valid for 24 hours.
import requests
def get_token_by_refresh(refresh_token):
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', data={'grant_type': 'refresh_token', 'refresh_token': refresh_token})
token, refresh_token = token.json()['access_token'], token.json()['refresh_token']
return token, refresh_token
Usage
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
token, refresh_token = get_token_by_refresh(refresh_token)
Getting authentication headers
The suggested function below will retrieve the authentication header that can be passed in your API calls.
import requests
username = "YOUR EMAIL"
password = "YOUR PASSWORD"
AppID = "YOUR APP ID"
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
Usage
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
API Endpoints
Quantexa News API includes endpoints that provide retrieval and analysis features, allowing you to search, collect, and analyze news content at scale. Each endpoint returns a different type of data. Click on each endpoint's documentation on the list to the left or search this page to find documentation on a specific parameter.
Endpoints specifications are available on GitHub YAML documentation repository.
Stories
The Stories endpoint enables you to search for news articles based on a specific set of parameters that you set in your query, such as keywords, entities, or sources. The News API gathers articles in near real-time and stores and indexes them along with metadata and enrichments, which you can search for.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/stories
Retrieving all stories
The suggested function below will retrieve all the stories that match your criteria.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_stories(params, headers):
# Fetch stories from the Aylien News API using the provided parameters and headers.
fetched_stories = []
stories = None
while stories is None or len(stories) > 0:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/stories', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
response_json = response.json()
stories = response_json['stories']
if 'next_page_cursor' in response_json.keys():
params['cursor'] = response_json['next_page_cursor']
else:
print('No next_page_cursor')
fetched_stories += stories
if len(stories) > 0 and not stories == None:
print(
'Fetched %d stories. Total story count so far: %d'
% (len(stories), len(fetched_stories))
)
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
print(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
return fetched_stories
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'published_at': '[NOW-14DAYS TO NOW]',
'language': '(en)',
'categories': '{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}',
'entities': '{{surface_forms:("Apple" OR "Tesla") AND overall_prominence:>=0.65}}',
'per_page': 100,
}
stories = get_stories(params, headers)
Retrieving top stories
The suggested function below will retrieve the stories that match your criteria until they reach a threshold. It will retrieve the top results for your query, which is useful for controlling the API response.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_top_stories(params, headers, n_top_stories=False):
fetched_stories = []
stories = None
if 'per_page' in params.keys():
if params['per_page'] > n_top_stories and not n_top_stories == False:
params['per_page'] = n_top_stories
while (
stories is None
or len(stories) > 0
and (len(fetched_stories) < n_top_stories or n_top_stories == False)
):
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/stories', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
response_json = response.json()
stories = response_json['stories']
if 'next_page_cursor' in response_json.keys():
params['cursor'] = response_json['next_page_cursor']
else:
pprint('No next_page_cursor')
fetched_stories += stories
if len(stories) > 0 and not stories == None:
print(
'Fetched %d stories. Total story count so far: %d'
% (len(stories), len(fetched_stories))
)
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
pprint(e)
break
return fetched_stories
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'published_at': '[NOW-14DAYS TO NOW]',
'language': '(en)',
'categories': '{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}',
'entities': '{{surface_forms:("Apple" OR "Tesla") AND overall_prominence:>=0.65}}',
'per_page': 100,
}
stories = get_top_stories(params, headers, 300)
Time series
Time series allows you to track changes in quantitative values contained in stories over time. This information can be anything from mentions of a topic or entities, sentiment about a topic, or the volume of stories published by a source, to name but a few. Using the Date Math Syntax Date Math Syntax, you can easily set your query to return information from any time period, from the current point in time to when Quantexa News API started collecting stories. The returned information can be rounded to a time you also specified, for example, by setting the results into hourly, daily, or weekly data points.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/time_series
Retrieving time series
The suggested function below will retrieve all the time series aggregations that match your criteria.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_timeseries(params, headers):
# Make a GET request to the Aylien News API to retrieve a time series of news articles based on the given parameters and headers.
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/time_series', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
timeseries = response.json()
return timeseries
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'published_at': '[NOW-14DAYS TO NOW]',
'language': '(en)',
'categories': '{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}',
'period': '+14DAYS',
}
timeseries = get_timeseries(params, headers)
Clusters
The Clusters endpoint is used to retrieve cluster objects. A cluster object includes a unique cluster ID, some metadata about the cluster, and a story that best represents the cluster. Stories associated with a cluster can be retrieved by calling the Stories endpoint with the cluster ID supplied as the cluster parameter.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/clusters
Retrieving clusters
The suggested function below will retrieve clusters that match your criteria.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_clusters(params, headers):
# Make a GET request to the Aylien News API to retrieve news clusters based on the provided parameters and headers.
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/clusters', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
fetched_clusters = response.json()
return fetched_clusters['clusters']
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'story_count': '[20 TO 100]',
'earliest_story.start': '2023-09-01T00:00:00Z',
'earliest_story.end': '2023-09-01T23:59:59Z',
'latest_story.start': '2023-09-14T00:00:00Z',
'latest_story.end': '2023-09-14T23:59:59Z',
'location.country': 'US',
}
clusters = get_clusters(params, headers)
Trends
Trends allow you to identify the most frequent values for categorical attributes contained in stories, e.g., the most frequent entities, concepts, or keywords. This endpoint allows you to set parameters like a time period, a subject category, or an entity, and it will return the most mentioned entities or keywords that are mentioned in relation to your query.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/trends
Retrieving trends
The suggested function below will retrieve the trends that match your criteria.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_trends(params, headers):
# Make a GET request to the Aylien News API to retrieve the current news trends based on the provided parameters and headers.
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/trends', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
trends = response.json()
return trends
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'published_at': '[NOW-14DAYS TO NOW]',
'language': '(en)',
'categories': '{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}',
'field': 'entities.body.surface_forms.text',
}
trends = get_trends(params, headers)
Autocompletes
Autocomplete is a helper endpoint that enables you to search for entities and sources in the Quantexa News API database. It takes a search term and returns suggestions, which then can be leveraged as search parameters in your News API query. For example, let's say you want to search the news for the company “Apple”, running a query to the Autocomplete endpoint will return a list of entities where they exist, including the entity id {'id': 'Q312', 'text': 'Apple Inc.'}. This entity ID can then be used to search the News API and filter for news specifically on the company since it has been trained in the knowledge base.
Autocomplete types
The Autocomplete endpoint allows you to search for different fields from the database:
entity-types - Search entity types to filter by for disambiguation.
entity-names - Search the entity knowledge base for organizations, people, locations and much more.
sources - Search news publishers from sources inventory.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/entity-types
GET https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/entity-names
GET https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/sources
Retrieving entity types
The suggested function below will retrieve the entity types associated with the entity searched.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_autocompletes_entity_types(params, headers):
# Make a GET request to the Aylien API to retrieve autocomplete suggestions for entity types.
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/entity-types', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
types = response.json()
return types
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {'term': 'organization',
'limit': 3}
entity_types = get_autocompletes_entity_types(params, headers)
Retrieving entities
The suggested function below will retrieve entities available in the knowledge base that approximate the term passed.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_autocompletes_entity_names(params, headers):
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/entity-names', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
entities = response.json()
return entities
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {'term': 'Apple',
'type_id': 'Q43229',
'limit': 3}
entity_names = get_autocompletes_entity_names(params, headers)
Retrieving sources
The suggested function below will retrieve sources available on the knowledge base that approximate the term passed.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_autocompletes_sources(params, headers):
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v2/autocomplete/suggestions/sources', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
sources = response.json()
return sources
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {'domain_term': 'bbc.com',
'limit': 3}
sources = get_autocompletes_sources(params, headers)
Histograms
Histograms allow you to retrieve a histogram snapshot of any quantitative attribute of articles that match your query. The histogram will show the distribution of articles over a range of values for your specified parameter. For example, to understand how long articles written by a particular journalist are on average, you can use Histograms and specify the journalist's name using author.id[] or author.name, then set the field value to words_count to retrieve a histogram that shows how many of this author's articles are and how long (in words). You can also specify the histogram's start and endpoints, as well as the bin width interval.start, interval.end, and interval.width, respectively.
HTTP Request URL
GET https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/histograms
Retrieving histograms
The suggested function below will retrieve the related stories that match your criteria.
import requests
import time
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppID = 'YOUR APP ID'
def get_auth_header(username, password, appid):
# Generate the authorization header for making requests to the Aylien API.
token = requests.post('https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token', auth=(username, password), data={'grant_type': 'password'})
token = token.json()['access_token']
headers = {f'Authorization': 'Bearer {}'.format(token), 'AppId': appid}
return headers
def get_histograms(params, headers):
while True:
try:
response = requests.get('https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/histograms', params=params, headers=headers)
# If the call is successfull it will append it
if response.status_code == 200:
histograms = response.json()
return histograms
# If the application reached the limit per minute it will sleep and retry until the limit is reset
elif response.status_code == 429:
time.sleep(10)
continue
# If the API call face network or server errors it sleep for few minutes and try again a few times until completely stop the script.
elif 500 <= response.status_code <= 599:
time.sleep(260)
continue
# If the API call return any other status code it return the error for futher investigation and stop the script.
else:
pprint(response.text)
break
except Exception as e:
# In case the code fall in any exception error.
print(e)
break
The code block below demonstrates how to use the function above.
headers = get_auth_header(username, password, AppID)
params = {
'published_at': '[NOW-14DAYS TO NOW]',
'language': '(en)',
'categories': '{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}',
'entities': '{{surface_forms:("Apple" OR "Tesla") AND overall_prominence:>=0.65}}',
'interval.start': 1200,
'interval.end': 5000,
'field': 'source.rankings.alexa.rank',
}
histograms = get_histograms(params, headers)
AQL
AQL is a Lucene-based syntax that enables users to perform powerful searches. Queries in this syntax are made within an aql parameter.
Status codes & Responses
2XX - Success
Status codes from 200 to 299 mean your call was successful.
| 200 | 'OK' Success. Your API call was processed fine. |
4XX - Request status
The 4XX codes are intended for cases in which the call seems to have erred. It could be either due to credentials or bad parameters sent with the API call.
| 400 | 'Bad Request' The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error. |
| 401 | 'Unauthorized' Authentication credentials were missing or the token may have expired. For further clarification contact your account manager. |
| 403 | 'Forbidden' Your plan does not have access to the feature you requested. More details about the missing feature are provided in the response message. For further clarification contact your account manager. |
| 404 | 'Not Found' The URI requested is invalid or the resource requested, such as a story, does not exist. For endpoints URLs follow the link to API endpoints page. |
| 405 | 'Method Not Allowed' A request method is not supported for the requested resource. For endpoints methods allowed follow the link to API endpoints page. |
| 414 | 'Request URI Too Long' The URL provided was too long for the server to process. The maximum URL length allowed for GET method size is 8 KB, or depending on the set approximately 8 thousand characters. |
| 422 | 'Unprocessable Entity' The request was invalid or cannot be otherwise served. For allowed values on API class, follow the link to parameters and common workflows. |
| 429 | 'Too Many Requests' Usage limits are exceeded. For more details on how limits works follow the link to pagination. Or further clarification contact your account manager. |
5XX - Network or Server status
5XX codes relate to requests that should be valid, but are unable to be fulfilled.
| 500 | 'Internal Server Error' An unexpected error has occurred, and our engineers have been informed. If the issue persists, contact the technical support team. |
| 503 | 'Service Unavailable' The server is currently unavailable, or it exceeds the attempts with the same URL. For more details on how to paginate through results, follow the link to pagination. |
| 504 | 'Gateway Timeout' The server could not get a response in time, probably because the client is blocked or behind a firewall. |
Rate limits
The API's rate limiting is primarily considered per application, with two limits applied per application ID.
Hits rate limit
Each endpoint is subject to a rate limit of 60 hits per minute or three hits per second.
Volumes rate limit
This is the allowance of how many stories can be pulled by the application from the /stories endpoint. The limited volumes of stories only apply to the count of stories retrieved from the endpoint stories.
This limit is applied for each application ID. It goes along with the plan acquired. Most commonly, the limit per month period or unlimited, where no limit is applied.
Handling the exceeded rate limit
Quantexa News API will return an HTTP 429 "Too Many Requests" response code when an application exceeds the rate limit for a given API endpoint.
{
"errors":[
{
"code":"KB429",
"detail":"You've exceeded your hits per minute rate limit. On the News API plan you can't make more than 60 hits per minute. Current usage stats: 62/60 hits per minute. Please follow the rate limit guidelines at the following link: https://docs.aylien.com/newsapi/v6/#rate-limits.",
"id":"error429_too_many_request",
"links":{
"about":"https://docs.aylien.com/newsapi/v6/#rate-limits"
},
"status":429,
"title":"Too Many Requests"
}
]
}
Tracking the hit and volume rates
There are three response headers with the quota allowance, the number of hits remaining on your quota, and when it will be reset.
import requests
from pprint import pprint
username = 'YOUR EMAIL'
password = 'YOUR PASSWORD'
AppId = 'YOUR APP ID'
token = requests.post("https://api.aylien.com/v1/oauth/token", auth=(username, password), data={"grant_type": "password"}).json()["access_token"]
headers = {f"Authorization": "Bearer {}".format(token),
"AppId":AppId}
url = 'https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/time_series'
#Submitting a date range through an array flat parameter
params ={
'published_at[]':'[NOW-3DAY TO NOW-2DAY]',
'language':'en'
}
response = requests.get(url,params=params, headers=headers)
pprint(response.headers)
Response
{'content-encoding': 'gzip',
'content-length': '143',
'content-type': 'application/json',
'date': 'Tue, 05 Sep 2023 16:40:32 GMT',
'server': 'istio-envoy',
'vary': 'Accept-Encoding',
'x-envoy-upstream-service-time': '303',
'x-powered-by': 'Gateway/v0.0.7-292-g40bef9e',
'x-ratelimit-hit-limit': '60',
'x-ratelimit-hit-period': 'minute',
'x-ratelimit-hit-remaining': '59',
'x-ratelimit-hit-reset': '2023-09-05 16:34:00 +0000',
'x-ratelimit-limit': '60',
'x-ratelimit-remaining': '59',
'x-ratelimit-reset': '2023-09-05 16:34:00 +0000',
'x-ratelimit-volume-limit': '100000',
'x-ratelimit-volume-period': 'month',
'x-ratelimit-volume-remaining': '98158',
'x-ratelimit-volume-reset': '2023-10-01 00:00:00 +0000',
'x-request-id': '2ae977ff-f8a9-4677-b4b2-5c7591d009af',
'x-request-time': '52 ms', 'x-version': '0.0.2-1402-g7e71e28c'}
'x-ratelimit-hit-limit': The number of allowed requests in the period.'x-ratelimit-hit-period': The period that the allowed requests can be used.'x-ratelimit-hit-remaining': The number of remaining requests in the current period.'x-ratelimit-hit-reset': The remaining window before the rate limit resets in UTC epoch seconds.
Rate limit reset
The News API request limit is based on a per-clock-minute window but not on a 60-second rolling window.
For example, from 12:11 pm to 12:12 pm, you can send 60 requests. At 12:12, this limit resets again. If 20 requests are sent to the API 30 seconds past 12:11 pm, then the remaining rate limit will be 40 hits left for that minute (i.e., for the next 30 seconds).
What happens if you get rate limited a lot?
If you continually get rate-limited, we may block your application or IP. For repeat offenders, we may block your other applications as well and disallow you from creating new applications, so be sure to get in touch with our support team if you're getting rate-limited frequently.
URL encoding
Quantexa News API can be accessed in many ways. It can either be accessed via programming languages like Python, JS, command cURL, or any other language that supports HTTP method calls or even via development platforms like Postman, but all the HTTP API calls must be encoded in URL no matter the language or platform used.
The following examples show how queries can be properly encoded.
Requests library
Below are the parameters in a dictionary object that can be passed as parameters on the GET requests function.
params = {
"published_at": "[14DAYS TO NOW]",
"language": "(en)",
"categories": "{{taxonomy:aylien AND id:(ay.fin.stockups OR ay.fin.stkclose) AND score:>=0.65}}",
"entities": '{{surface_forms:("Apple" OR "Tesla") AND overall_prominence:>=0.65}}',
"per_page": 100,
}
URL encoded
https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/stories?published_at=%5B14DAYS+TO+NOW%5D&language=%28en%29&categories=%7B%7Btaxonomy%3Aaylien+AND+id%3A%28ay.fin.stockups+OR+ay.fin.stkclose%29+AND+score%3A%3E%3D0.65%7D%7D&entities=%7B%7Bsurface_forms%3A%28%22Apple%22+OR+%22Tesla%22%29+AND+overall_prominence%3A%3E%3D0.65%7D%7D&per_page=100
Postman
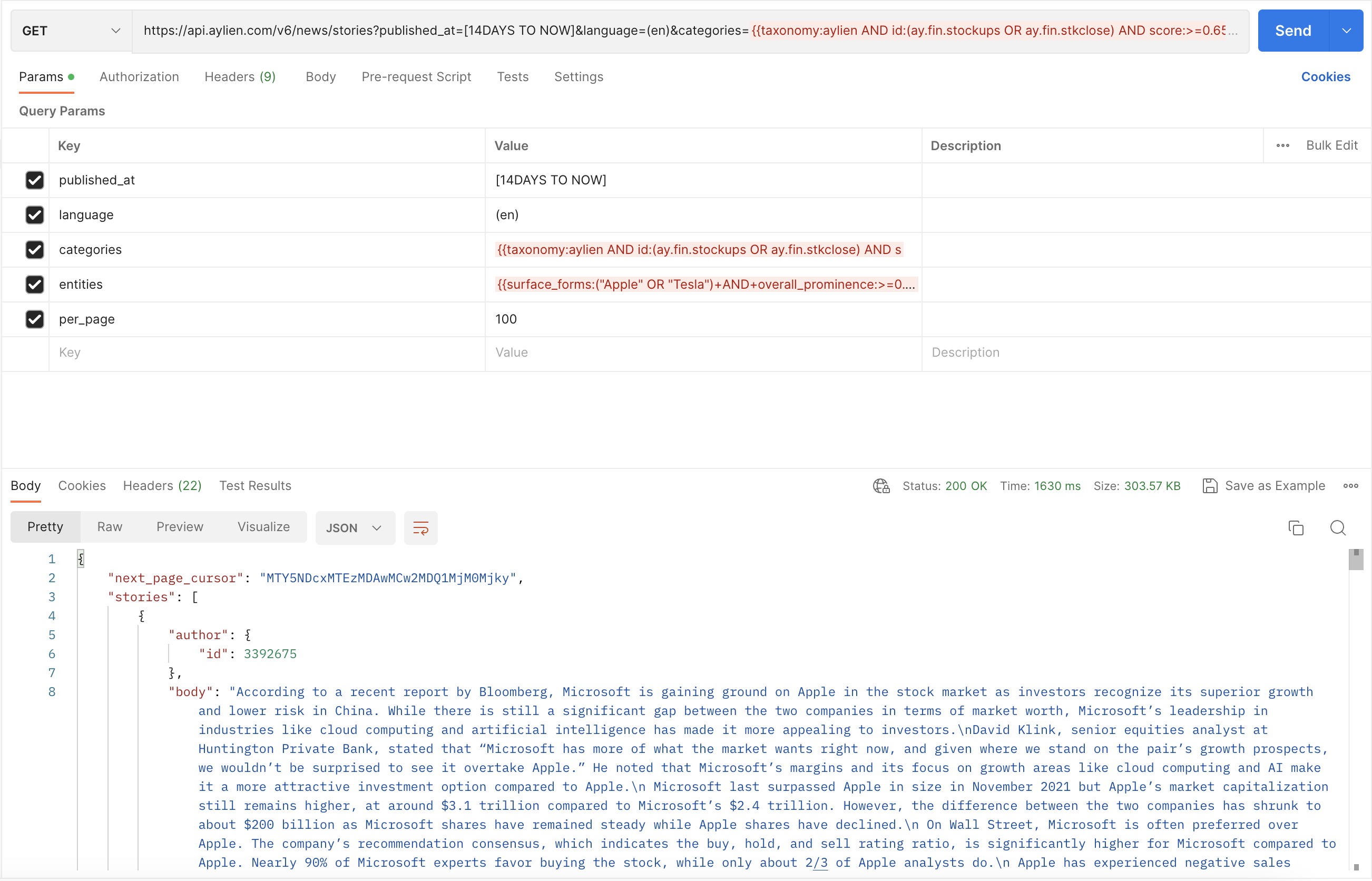
URL encoded
https://api.aylien.com/v6/news/stories?published_at=%5B14DAYS+TO+NOW%5D&language=%28en%29&categories=%7B%7Btaxonomy%3Aaylien+AND+id%3A%28ay.fin.stockups+OR+ay.fin.stkclose%29+AND+score%3A%3E%3D0.65%7D%7D&entities=%7B%7Bsurface_forms%3A%28%22Apple%22+OR+%22Tesla%22%29+AND+overall_prominence%3A%3E%3D0.65%7D%7D&per_page=100
Language support
The News API sources content from across the globe in 16 languages.
All content is available in its native form and also machine-translated English text.
The multiple (human) languages supported can be selected using the language parameter.
English (en) |
German (de) |
French (fr) |
Italian (it) |
Spanish (es) |
Portuguese (pt) |
Russian (ru) |
Dutch (nl) |
Arabic (ar) |
Turkish (tr) |
Traditional Chinese (zh-tw) |
Simplified Chinese (zh-cn) |
Swedish (sv) |
Danish (da) |
Finnish (fi) |
Farsi (fa) |
The NLP enrichments are performed on native English or translated English text. These enrichments include category and industry enrichment, entity extraction, and sentiment analysis. The table below lists the language used for analysis for each feature.
| Feature | Original Text Analyzed | Translated Text Analyzed |
|---|---|---|
| Clusters | en |
All Other Languages |
| Topic Categories | en |
All Other Languages |
| Entities | en |
All Other Languages |
| Sentiment (body) | en, es, de |
All Other Languages |
| Extracted Keywords | en, es, de, it, fr, pt |
All Other Languages |
| Hashtags | en, es, de, it, fr, pt |
All Other Languages |
| Word, Character, and Paragraph Counts | en, es, de, it, fr, pt |
All Other Languages |
Licensed content
Customers with access to licensed content can retrieve articles from both licensed and publicly available sources. The license_type field in the stories endpoint response specifies the content rights classification, indicating whether an article is categorized as licensed or public web content.
License content flag on API response
This field is a non-blank binary Boolean field. It will always return either the value 0 or 1.
license_type 0 - Indicates the story is from a group of web-based, openly accessible sources
[ ...
{'license_type': 0}
...
]
license_type 1 - Indicates the story is from the group of licensed sources
[ ...
{'license_type': 1}
...
]
